These AI tools Will Change How You Design UX Forever. Are You Ready?
Artificial Intelligence isn’t just the future — it’s here, and it’s reshaping how we design experiences. In the world of UX design, AI is more than a buzzword; it’s a game-changer, revolutionizing how designers create intuitive, user-focused interfaces. Imagine automating tedious tasks, generating wireframes in seconds, and tailoring experiences to individual users — all in real-time.
But with great power comes great responsibility. As AI tools rise to prominence, they bring transformative opportunities alongside ethical dilemmas and creative challenges. In this post, we’ll dive deep into how AI is transforming UX design, explore groundbreaking tools, and confront the controversies shaping this new frontier. Whether you’re a seasoned designer or just curious about what’s next, this is the ultimate guide to understanding AI’s impact on UX.
Exploring the Benefits of AI in UX Design
Automating Repetitive Tasks
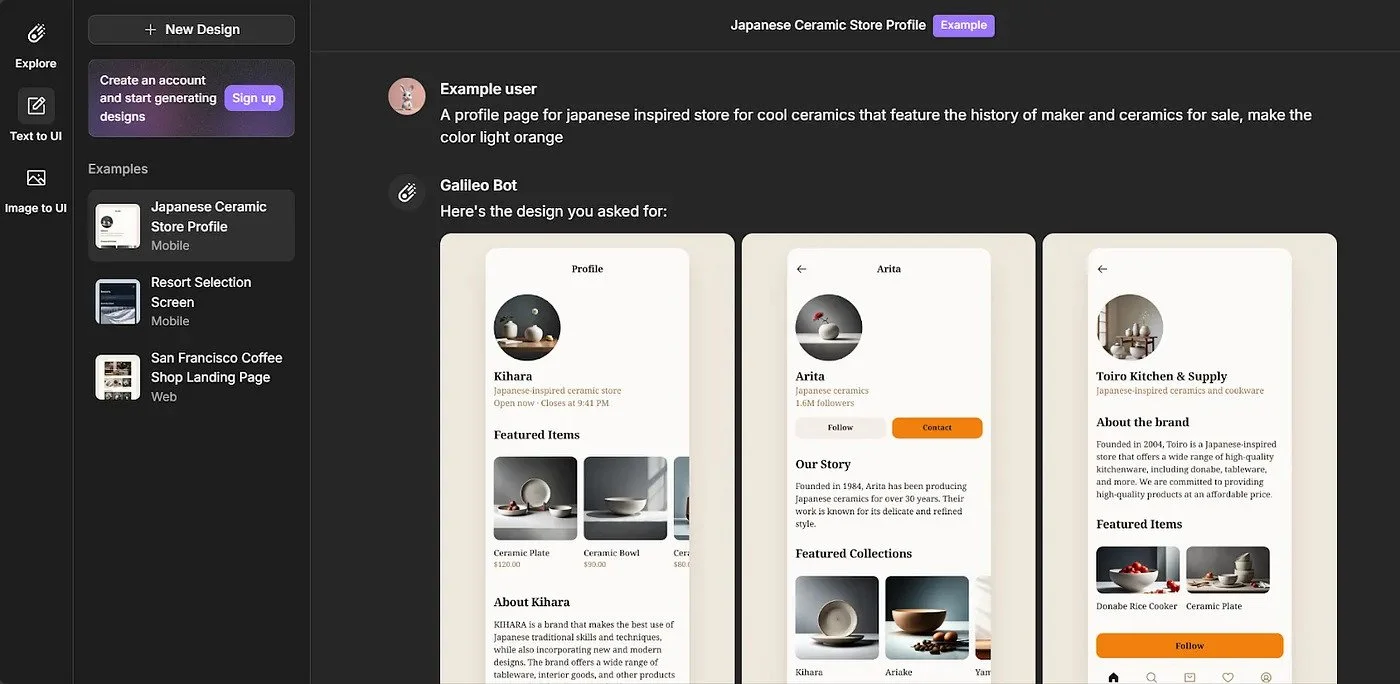
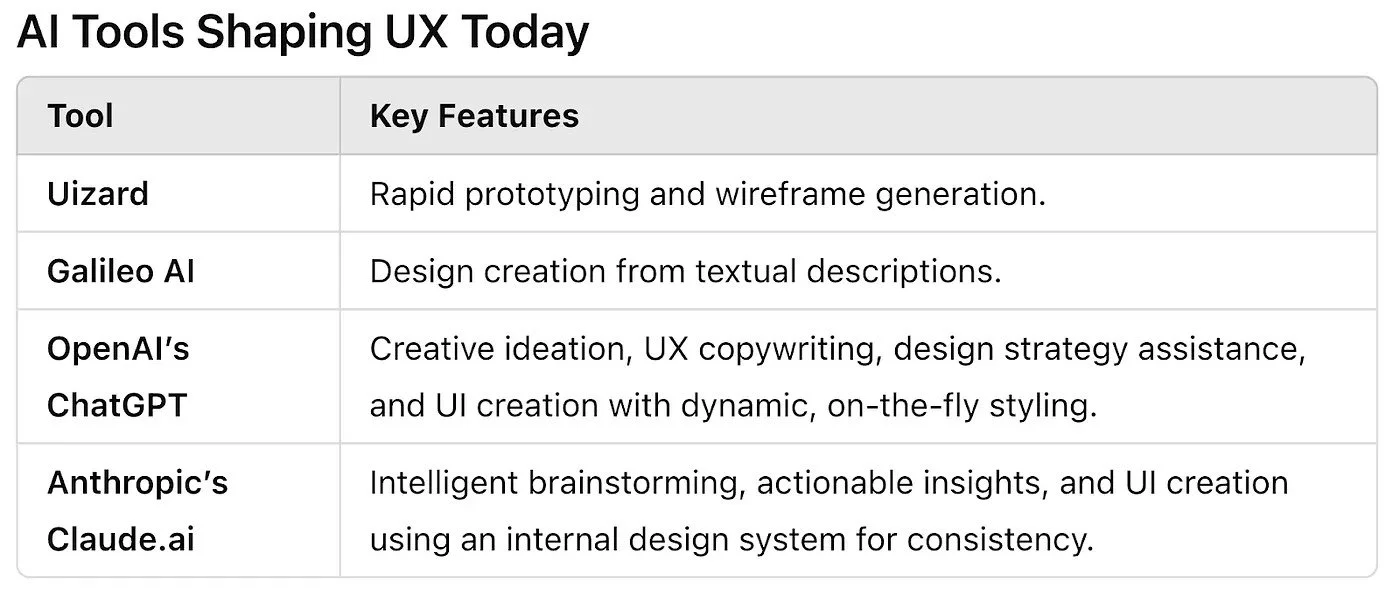
AI accelerates processes like wireframing and usability testing, allowing designers to focus on high-value tasks. Tools like Uizard and Galileo AI can transform text prompts into wireframes or designs in seconds, offering a glimpse into the future of automated design workflows. These tools save countless hours by eliminating the need to create designs from scratch, allowing designers to iterate quickly and experiment with multiple variations in record time.
AI also integrates seamlessly with other tools, making it easier to manage end-to-end workflows. For instance, designers can use AI-powered platforms to auto-generate style guides, adapt layouts for various screen sizes, or suggest improvements based on usability heuristics. This holistic approach not only speeds up design cycles but also ensures consistency and scalability across projects.
Galileo AI constructs a profile page.
Personalized Experiences
Leveraging user data, AI crafts personalized journeys that boost engagement. For instance, e-commerce platforms like Sephora use AI-driven algorithms to recommend products tailored to individual preferences. AI enables real-time customization, such as dynamically adapting web layouts or displaying personalized content based on user behavior and preferences.
In addition to retail, other industries like healthcare use AI to offer tailored experiences. For example, fitness apps provide personalized workout plans and nutrition tips by analyzing user data, such as goals and past activity. This level of customization builds stronger user connections, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement.
Empowering Independent Design
AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Anthropic’s Claude.ai go beyond just providing insights — they act as creative collaborators. Designers can use these platforms to generate design ideas, write compelling UX copy, or even outline workflows, enabling them to bring their visions to life with minimal external support.
These tools are especially valuable for solo designers or small teams, offering an extra layer of support that would typically require larger resources. For example, ChatGPT can assist in brainstorming design ideas or crafting user personas, while Claude.ai excels at structuring complex workflows or refining design strategies for clarity and impact.
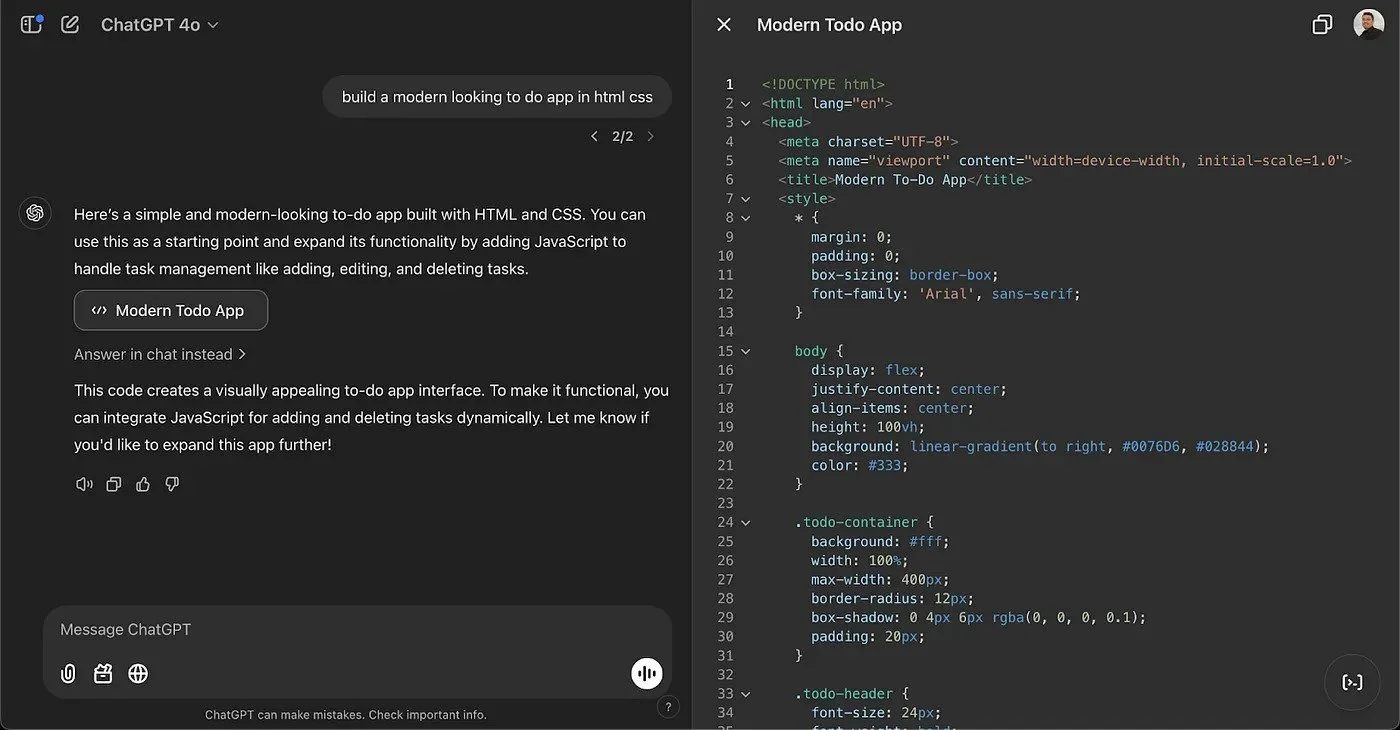
A unique distinction between these tools is their approach to design generation. Anthropic’s Claude.ai builds UI elements using its internal design system, ensuring consistency and adherence to established patterns, making it ideal for maintaining brand alignment. Conversely, ChatGPT dynamically generates styling on the fly, offering more flexibility for creative exploration and novel design ideas.
Furthermore, these AI platforms are adept at integrating into iterative design processes. Designers can present rough concepts, receive constructive feedback, and adjust their work in real time. This dynamic collaboration enables faster prototyping and more innovative outcomes.
Claude AI makes a modern to-do app.
ChatGPT makes a modern to-do app.
All the best current AI tools for UX as of Dec 2024.
Real-World Applications of AI in UX
Personalization in E-Commerce
Companies like Amazon and Sephora have integrated AI to deliver personalized shopping experiences, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. AI systems analyze customer data to make real-time product recommendations, optimize pricing strategies, and even predict future purchases based on browsing patterns and preferences. This creates a seamless and engaging shopping experience tailored to each user.
User Behavior Analysis
Tools like Hotjar use AI to provide heatmaps and session recordings, offering insights into user behavior that guide data-driven decisions. These tools enable designers to identify bottlenecks in user flows, understand how users interact with various elements, and prioritize updates to improve usability. AI can also detect patterns that might be missed by manual analysis, helping teams create more intuitive and efficient designs.
Accessibility Improvements
AI identifies barriers for users with disabilities, suggesting solutions for inclusive design. For instance, AI can analyze website content to detect and address issues like insufficient contrast ratios, missing alt text, or poorly structured navigation. Additionally, AI-driven tools can generate alternative text descriptions for images, translate text into multiple languages, or even provide real-time sign language translation, making digital platforms more accessible to a diverse audience. This fosters equity and ensures compliance with accessibility standards.
Figma’s AI Controversy
Apple’s weather app (left) & figma’s AI generated design (right)
Figma recently introduced an AI-powered feature called “Make Design,” designed to generate user interface layouts from text prompts. However, the tool faced immediate criticism when users noticed that, upon prompting it to create a weather app, it produced designs strikingly similar to Apple’s Weather app on iOS. Andy Allen, founder of NotBoring Software, highlighted this issue by sharing examples where the AI-generated designs closely mirrored Apple’s interface. This led to accusations that Figma’s AI had been trained on existing app designs without proper authorization.
In response, Figma’s CEO, Dylan Field, denied these allegations, stating that the “Make Design” feature was not trained on Figma content, community files, or app designs. He attributed the issue to low variability in the underlying design systems used by the AI. Consequently, Figma temporarily disabled the feature to conduct a comprehensive quality assurance review.
This incident underscores the challenges and ethical considerations in deploying AI within design tools, particularly concerning originality and potential intellectual property infringements. It highlights the necessity for rigorous testing and ethical guidelines to ensure AI-generated content does not inadvertently replicate existing designs.
Challenges of Integrating AI in UX
Ethical Concerns
Unchecked AI can perpetuate biases and compromise user privacy. Designers must approach AI adoption with responsibility to uphold trust and fairness.
Dependence on Automation
Over-reliance on AI risks diminishing creativity and human input in design processes. Balancing automation with hands-on design is critical.
Complex Implementation
Implementing AI requires expertise and resources, which can pose challenges for smaller teams or organizations.
Future Opportunities for AI in UX
Adaptive Interfaces
AI can create interfaces that evolve based on user behavior, offering personalized and contextually relevant experiences. By analyzing patterns in how users interact with a platform, AI can predict needs and adjust layouts, features, or content accordingly.
For example, in e-commerce, an adaptive interface might showcase product categories based on a user’s browsing history or prioritize frequently visited sections for quicker access. Similarly, in educational platforms, AI can tailor learning paths to an individual’s progress and challenges, ensuring a more effective and personalized experience.
Adaptive interfaces also extend to dynamic user roles, where the platform customizes workflows for different types of users, such as administrators, contributors, and end-users. This flexibility not only enhances user satisfaction but also boosts overall engagement and efficiency.
Enhanced Collaboration
By providing data-driven insights, AI fosters collaboration between designers, developers, and stakeholders, bridging communication gaps. AI can act as a mediator in design discussions by providing objective data, such as user engagement metrics or predicted outcomes of design changes, which helps align cross-functional teams.
For instance, tools like ChatGPT or Claude.ai can generate user scenarios or explain technical constraints in plain language, making it easier for designers and developers to stay on the same page. Additionally, AI-driven platforms can consolidate feedback from multiple stakeholders, prioritize key issues, and suggest actionable steps, streamlining the iterative process. This collaborative efficiency not only saves time but also fosters a shared vision among all contributors.
AR/VR Integration
The fusion of AI with AR/VR technologies promises immersive, next-level user experiences. These innovations could redefine how users interact with digital environments. For instance, AI-powered AR applications can enable real-time object recognition and contextual overlays, enhancing productivity in fields like education, healthcare, and industrial design.
In virtual reality, AI allows for dynamic, responsive environments that adapt to user behavior. Imagine training simulations that evolve based on individual performance, offering tailored challenges and feedback. Moreover, AI can streamline content creation for AR/VR by automating tasks such as 3D modeling and scene generation, reducing production time and costs.
These advancements make AR/VR experiences more intuitive, engaging, and accessible, paving the way for groundbreaking innovations in user interaction and immersive storytelling.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing UX design by offering unprecedented efficiency, personalization, and insight. Tools like ChatGPT and Claude.ai empower designers to bring their ideas to life independently, reshaping the creative process. They enable everything from rapid prototyping to personalized interfaces and adaptive workflows, allowing designers to work smarter and focus on creativity. These advancements ensure that users receive tailored, inclusive, and contextually relevant experiences that evolve with their needs.
However, the journey isn’t without challenges. Designers must address ethical concerns, such as bias in AI models and user privacy, while maintaining a balance between automation and human creativity. Navigating these challenges thoughtfully is key to unlocking the full potential of AI-driven UX design.
By integrating AI strategically, designers can push the boundaries of what’s possible, creating next-generation interfaces that are both innovative and impactful. What’s your take on AI’s role in UX design? Have you tried tools like ChatGPT or Claude.ai in your workflows? Share your thoughts, experiences, and visions for the future in the comments below!